Diabetic Neuropathy & Foot Care
When going to see a medical professional, such as a primary care physician or physical therapist, you may hear them ask, “Do you have any numbness and tingling?” Although there is an array of causes of numbness and tingling, one of the most prevalent causes in our society is diabetic neuropathy.
So, what exactly is diabetic neuropathy and how do I get it?
Diabetic neuropathy occurs when there is excess sugar in the blood, which is a staple of uncontrolled diabetes. Prolonged exposure of elevated blood sugar can cause significant damage to the nerve and the blood vessels that supply the nerve with oxygen. When this nerve is damaged, it is unable to send signals or sends impaired signals back to the brain about that body part. This will eventually result in numbness or tingling.
What else does this effect?
These impaired signals or lack thereof may also result in loss of balance and coordination from decreased proprioception (awareness of one’s body in space). In some cases, it can eventually effect the motor component of the muscle resulting in muscle weakness.
Where Does Diabetic Neuropathy Occur?
Diabetic neuropathy can occur anywhere in the body. Even though diabetic neuropathy may occur anywhere, it mostly affects the extremities (limbs). Most commonly it will affect the sensation of the feet. The course of diabetic neuropathy is that it will typically start distally, or furthest away from the body. For example, initially this numbness may start in the toes and overtime if blood sugar levels continue to be uncontrolled it will work its way up the leg to the ankle, then calf, etc.
How is Diabetic Neuropathy Diagnosed?
Diabetic neuropathy is typically diagnosed according to someone’s symptoms, medical history, and a physical exam. The Physical exam may include, but is not limited to:
Monofilament test: Assesses the sensitivity to touch with a standardized nylon fiber or “monofilament”
Nerve Conduction Studies: A test that shows the velocity or speed of the nerves
EMG (electromyography): Assesses the electrical activity produced by the nerve in a particular muscle
Vibration and Temperature: How well the nerves can respond to vibration and changes in temperature
The Importance of Foot Care with Diabetic Neuropathy:
As stated before, diabetic neuropathy most commonly affects the nerves in a person’s feet. This altered sensation will significantly reduce the ability to sense pain in the feet. When the ability to feel pain in the feet is taken away, a person becomes unaware of the damage they may be doing to their feet. For example, someone could be walking around with a rock in their shoe all day and have no idea. This would result in a significant wound on the bottom of their foot.
Common Complication with Diabetic Neuropathy
A coupling issue with diabetic neuropathy can be damage or occlusion (blocking) of the blood vessels that supply the tissues of the body. This damage or occlusion of the blood vessels can restrict the blood flow to the tissues. Blood flow doesn’t only bring oxygen to the tissues, but also an array of chemical factors that initiate and guide the healing process. So, putting these two together can create a huge issue.
So What “Huge Issue” Does This Create?
With decreased sensation, a person is unaware of potential damage they are doing to the soft tissue of their foot. This will result in a wound or ulcer. Now combined with a compromised vascular supply (blood flow) a person will have a significantly slowed or absent healing process. If a wound never heals it may continue to get worse or become infected. If this happens amputation may be considered to prevent the spreading of the wound or infection. One can now see why people with diabetes have such an increased risk for some variation of leg or foot amputations. Proper foot care can help in preventing or ceasing the progression of this.
Foot Care:
Foot care is the most important thing for someone with diabetic neuropathy to prevent further complications. The American Diabetes Association outlines some useful tips to assist people in proper foot care to protect them from further injury or complication.
These tips are:
Taking care of your diabetes: keeping blood sugar levels under control can prevent or slow the progression of the nerve and blood vessel damage.
Check your feet every day: check your feet morning and night for cuts, wounds, red spots, or blisters. If you are unable to see the bottom of your feet ask someone to assist you or use a mirror. Try setting an alarm on your phone to remind yourself everyday.
Shoes: be aware of tight fitting shoes that may cause harm to your skin, talk to a health professional about the correct shoes for you.
Wash your feet everyday: be sure to dry them.
Keep your skin soft and smooth: Occasionally use lotion on your feet, but not between your toes.
Regularly trim and file your toenails: this will prevent ingrown nails and cutting of your toes
Wear shoes and socks at all times: never walk barefoot. Wear shoes that are comfortable and not too tight. Also, always check your shoes for rocks or other debris before wearing.
Protect your feet from hot and cold: be careful of walking on hot pavement and always test the water temperature before putting your feet in it. You may cause damage to your feet without knowing.
Keep the blood flowing to your feet: regularly pumping your ankles and wiggling your toes will assist in increasing the flood flow to your feet.
For more information on tips visit: diabetes.org/diabetes
What Can a Physical Therapist Do For Your Diabetic Neuropathy and Foot Care?
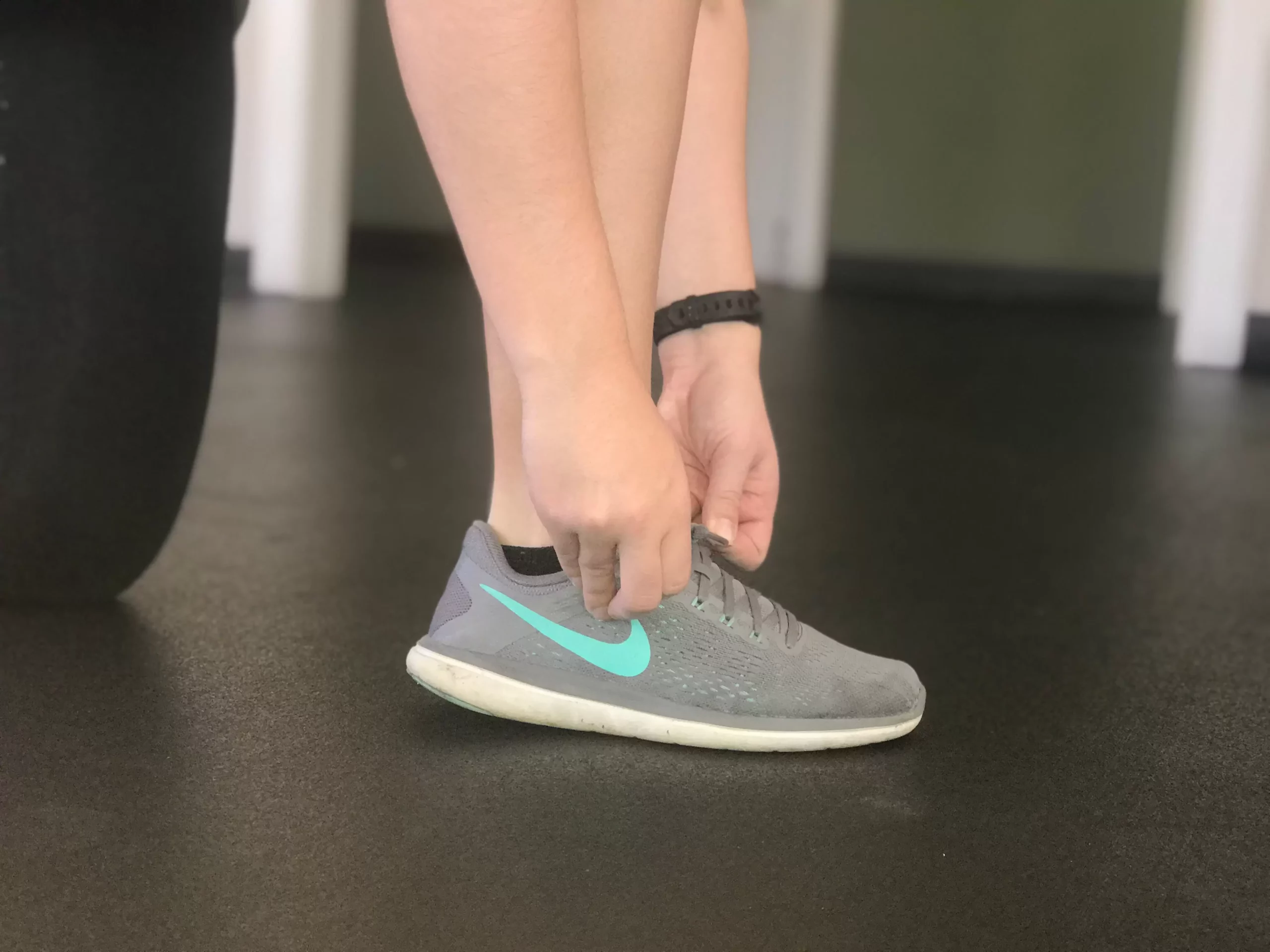
Foot Care and Shoe fitting
Physical therapists can directly assist in your foot care. They are able to help you decide on what kind of shoe is best for you. This may include proper arch support and fitting that will not decrease your circulation or cause harm to your feet. A physical therapist may also provide you with additional personalized foot care tips that directly apply to you and your lifestyle.
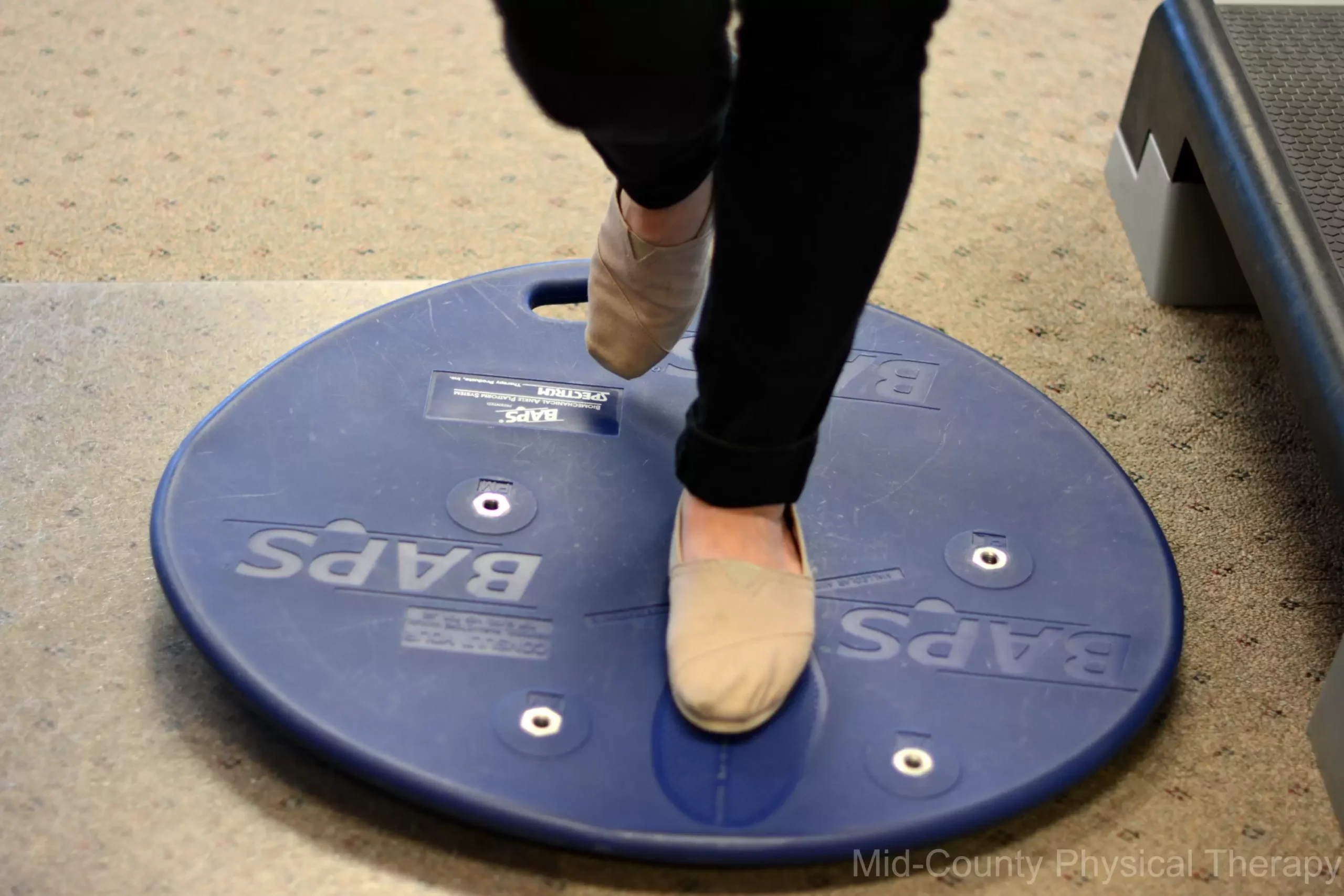
Preventing a Fall with Balance and Coordination Training
As mentioned before, diabetic neuropathy can have a profound effect on balance and coordination. In older populations and even younger ones, decreased balance and coordination can be a significant issue because it may result in a fall. A fall at any age can be devastating and cause not only physical harm, but also financial burden. Consulting a physical therapist can provide you with an individualized intervention to assist you in increasing your balance and coordination to decrease your risk of fall or injury.
Disclaimer
If you have a wound/ulcer or need assistance with the medical management of your diabetes or diabetic neuropathy you should consult your primary care physician on the steps you should take.
For more information on physical therapy and common orthopedic injuries visit us at our blog.
References


